🌘
Mysterious bones that date back seven million years likely belong to the oldest known human ancestor, according to a study published on Friday in Science Advances.
For years, scientists have debated whether Sahelanthropus tchadensis—an ape known from skull and limb bones found in Chad—was primarily bipedal, meaning that it walked on two legs like humans, or if it walked on all fours like chimpanzees.
Now, a team led by Scott Williams, an associate professor of anthropology at the Center for the Study of Human Origins at New York University, has spotted a detail in the femur bone, known as a femoral tubercle, that strongly suggests this ape was a biped. Since bipedalism is a defining trait of human relatives, known as hominins, the discovery confirms that these bones belonged to the earliest known human ancestor by a margin of about one million years.
“The really novel part of our study is the discovery of a new feature that had never been noticed before, and that’s the femoral tubercle,” Williams told 404 Media in a call. “I think that was the final piece of evidence that convinced me that this was a biped, and therefore probably a hominin, because you don’t find that feature in anything else.”
“I think this will convince a lot of people, but certainly not everyone,” he added. “There’ll be rebuttals. I’m sure that people will challenge it. That’s fine. That’s how science works.”
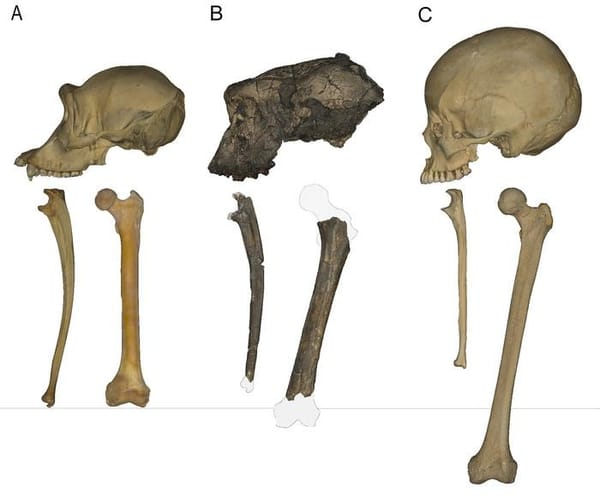
Indeed, the remains of Sahelanthropus tchadensis have generated controversy since they were initially reported in 2002. Over the past five years, different teams have argued both for and against the hypothesis that this species walked on two legs. This unresolved question inspired Williams and his colleagues to take a “fresh and independent look” at the fossils, he said.
The researchers conducted a comparison of the limb bones with other hominin remains, while also re-examining them using a technique called 3D geometric morphometrics. The latter effort exposed a hidden detail: the presence of a femoral tubercle, which is a bony protrusion where the femur connects to the hip.
“It basically prevents our torso from falling backward or falling sideways as we walk,” explained Williams. “Chimpanzees, gorillas, and other apes don’t need to have that structure because they don’t have to take on a vertical posture like we do. You don’t need that structure—unless you’re a biped.”
Of course, hominins didn’t just suddenly stand upright one day, and this ancient species shows an interesting mix of features that suggest it still spent plenty of time in the treetops in addition to walking on land. This liminal state between arboreal and terrestrial life persisted for millions of years in hominins until the rise of Homo erectus two million years ago, which is the first hominin to walk in a similar upright position to modern humans.
In addition to pinpointing our own human origins, the fossils offer a possible glimpse of the last common ancestor between humans and our closest living relatives, chimpanzees and bonobos. These two ape lineages split about six or seven million years ago, around the same time Sahelanthropus tchadensis was roaming through Chad.
“The debate about what the last common ancestor was like is really highly contested,” Williams said. The remains of Sahelanthropus tchadensis suggest that human relatives in this era may have been similar in size to chimpanzees and bonobos, but had body proportions more akin to later hominins.
While Sahelanthropus tchadensis can be described as the earliest human ancestor in a general sense, it was probably not the direct ancestor to modern humans. It’s become clear in recent decades that a diversity of hominin lineages emerged and became extinct over the past seven million years, so it’s difficult to trace the direct lineage of our own species, Homo sapiens, the only humans that have survived to the modern day.
“The more fossils that are discovered,” Williams said, “the more complicated the picture looks.”
